Essential Network Security Practices for Small Businesses in 2024

In today's digital landscape, small businesses face an unprecedented number of cybersecurity threats. With limited resources and IT expertise, implementing robust network security practices has become more critical than ever. This comprehensive guide outlines the essential security measures that can protect your business from costly data breaches and cyber attacks.
Understanding the Current Threat Landscape
Small businesses are increasingly targeted by cybercriminals due to their perceived vulnerabilities. According to recent studies, 43% of cyber attacks target small businesses, yet only 14% are prepared to defend themselves. The financial impact can be devastating, with the average cost of a data breach for small businesses reaching $2.98 million in 2024.
The most common threats include ransomware attacks, phishing campaigns, and unauthorized network access. These attacks often exploit weak network configurations and inadequate security protocols, making proper network security implementation crucial for business survival.
Firewall Configuration: Your First Line of Defense
A properly configured firewall serves as the cornerstone of network security. Modern firewalls go beyond simple packet filtering to provide deep packet inspection, application-layer filtering, and threat intelligence integration.
Essential Firewall Best Practices
- Default Deny Policy: Configure your firewall to deny all traffic by default, then explicitly allow only necessary connections
- Regular Rule Audits: Review and update firewall rules quarterly to remove outdated permissions
- Logging and Monitoring: Enable comprehensive logging to track all network activity and potential threats
- Geo-blocking: Restrict access from high-risk geographical locations unless business requirements dictate otherwise
Pro Tip: IP Scan Tools Integration
Utilize advanced ip scan tools to regularly audit your network perimeter and identify potential vulnerabilities in your firewall configuration. These tools can help detect open ports, misconfigured services, and unauthorized devices on your network.
Implementing Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)
Intrusion Detection Systems provide real-time monitoring of network traffic to identify suspicious activities and potential security breaches. For small businesses, implementing an effective IDS strategy involves both network-based and host-based detection systems.
Key IDS Components
Network-Based IDS (NIDS)
Monitors network traffic in real-time, detecting anomalies, scans, and malicious packet patterns across your entire network infrastructure.
Host-Based IDS (HIDS)
Monitors individual systems for file changes, unauthorized access attempts, and suspicious system behavior on critical servers and workstations.
Regular Security Audits: Maintaining Your Defense
Regular security audits are essential for maintaining an effective security posture. These comprehensive assessments help identify vulnerabilities, ensure compliance with security policies, and validate the effectiveness of implemented security controls.
Audit Frequency and Scope
| Audit Type | Frequency | Key Focus Areas |
|---|---|---|
| Network Vulnerability Scan | Monthly | Open ports, service versions, patch levels |
| Penetration Testing | Quarterly | External and internal attack simulations |
| Configuration Review | Bi-annually | Security settings, access controls, policies |
| Compliance Assessment | Annually | Regulatory requirements, industry standards |
Network Segmentation and Access Control
Proper network segmentation limits the potential impact of security breaches by isolating critical systems and controlling lateral movement within your network. This approach is particularly effective for small businesses with limited security resources.
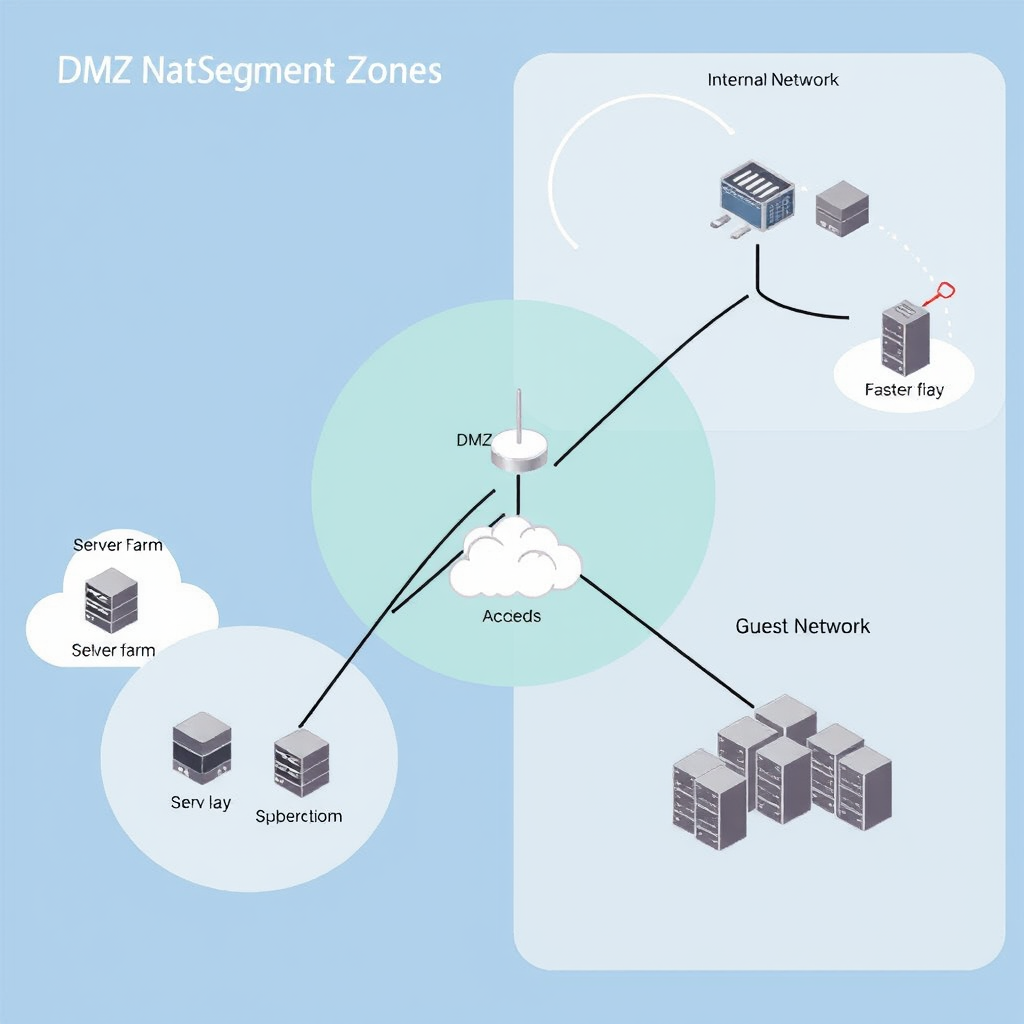
Segmentation Strategies
- DMZ Implementation: Create a demilitarized zone for public-facing services
- VLAN Separation: Use virtual LANs to isolate different business functions
- Guest Network Isolation: Separate visitor access from internal business networks
- Critical Asset Protection: Isolate servers containing sensitive data and financial information
Employee Training and Security Awareness
Human error remains one of the leading causes of security breaches. Implementing comprehensive security awareness training helps employees recognize threats and respond appropriately to potential security incidents.
Critical Training Topics
- Phishing email identification and reporting procedures
- Strong password creation and multi-factor authentication
- Safe browsing practices and software download policies
- Incident reporting protocols and emergency response procedures
Backup and Disaster Recovery Planning
A comprehensive backup and disaster recovery plan ensures business continuity in the event of a security incident. The 3-2-1 backup rule remains the gold standard: maintain three copies of critical data, store them on two different media types, and keep one copy offsite.
Recovery Time Objectives
Establish clear recovery time objectives (RTO) and recovery point objectives (RPO) for different business functions. Critical systems should have RTOs of less than 4 hours, while less critical systems may tolerate longer recovery times.
Monitoring and Incident Response
Effective security monitoring requires continuous oversight of network activities, system logs, and security alerts. Small businesses should implement automated monitoring solutions that can detect and respond to threats in real-time.
24/7 Monitoring
Continuous surveillance of network traffic and system activities
Alert Management
Automated threat detection and notification systems
Rapid Response
Quick incident containment and remediation procedures
Conclusion: Building a Resilient Security Framework
Implementing comprehensive network security practices requires ongoing commitment and regular updates to address evolving threats. Small businesses that invest in proper security infrastructure, employee training, and regular audits significantly reduce their risk of experiencing costly security breaches.
Remember that network security is not a one-time implementation but an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring, updating, and improvement. By following these essential practices and leveraging advanced ip scan tools for regular network assessments, small businesses can build robust defenses against modern cyber threats.
Take Action Today
Start by conducting a comprehensive network security assessment using professional ip scan tools to identify current vulnerabilities. Then prioritize implementing the security measures outlined in this guide based on your business's specific risk profile and available resources.